What is ISO?
ISO is the International Organization for Standardization, it is Non-Governmental Organization that structures an extension between the public and private divisions, Its work from Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland and was established in 1947 to create basic worldwide benchmarks in numerous regions. ISO is a system of the national guidelines establishments of with 163 part's nations.
What is ISO 45001? Are you looking for a simple answer to this question?
This question arises very often and this overview is meant to provide you with information on the benefits of ISO 45001 as well as the requirements of the standard, its structure and the steps towards certification.
Origins of ISO 45001:
ISO 45001, Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems – Requirements with guidance for use, is an ISO standard for occupational health and safety management systems that is recognized and implemented worldwide. This standard was published in 2018 in order to replace OHSAS 18001:2007.
Before the development of a management system standard by the ISO committee, a “Justification Study” was prepared in order to present a case for the proposed project. In relation to the development of ISO 45001, user needs are identified from the following:
- User demands for the requirements of management system standards to be better aligned, or to enable “integration” into their organization’s management systems. This led to the development of a “High Level Structure” (often referred to as “Annex SL”) which provides a common clause sequence (structure), text, terms and definitions for its management system standards. This “High Level Structure” has been applied during the development of ISO 45001.
- According to the OHSAS Project Group’s 2011 Survey of standards and certificates, there are now more than 90000 certificates issued in 127 countries. This fact demonstrates the need for an ISO standard for this discipline.
The “Justification Study” identified that ISO 45001 would need to:
- Enable organizations to provide safe and healthy working environments.
- Be generic and relevant to all types and sizes of organizations, operating in any sector, and be able to accommodate diverse geographical, cultural and social conditions
- Be capable of being applied to the widest possible range of organizations with varying degrees of maturity of their OH&SMS
- Specify the essential components of an OH&SMS
- Enable organizations to demonstrate conformity to the requirements
- Enable organizations to identify, assess, and control their OH&S risks and improve their OH&S performance.
- Align with other management system standards (in particular ISO 14001 for environmental management systems).
What is an Occupational Health & Safety Management System?
An Occupational Health & Safety Management System, often called an OH&SMS, defines the framework in which the organization cares for the occupational health and safety of its employees. It represents a set of rules, policies, processes, plans and practices for preventing occupational health and safety hazards and minimizes risks in the workplace. OH&SMS is unique for every organization and it must be adequate to the legal requirements, occupational health and safety hazards and business processes applied in the organization. ISO 45001 represents the best practices in establishing, implementing and maintaining the OH&SMS. Its requirements and guidelines help an organization to establish effective OH&SMS and to avoid missing important elements along this way.

Getting to the heart of why ISO 45001 is important
Mitigating occupational health and safety hazards and preventing injuries in the workplace is one of the most important challenges that companies face. Among the biggest benefits of implementing an OH&SMS is enhancement of company’s public image that comes with being ISO 45001 certified. Being certified against ISO 45001 demonstrates that your company belongs among those businesses that cares for its employees’ health and safety. This can bring better relationships with customers, the public, and the community, but it also brings other benefits.
Along with the good public image, many companies can save money through the implementation of an Occupational Health & Safety Management System. This can be achieved through reducing incidents resulting in injuries and being able to obtain insurance at a more reasonable cost. This improvement in cost control is a benefit that cannot be overlooked when you’re making the decision to implement an OH&SMS.
What does ISO 45001 actually look like?
The ISO 45001 consists of eleven sections. The first three sections represent an introduction to the standard, its scope and normative references, and the other seven sections contain the requirements for the Occupational Health and Safety Management System.
Here is what the seven main sections are about:
- Section 4:
Context of the organization
This section requires the organization to determine its context in terms of the Occupational Health and Safety Management System, including interested parties and their needs and expectations. It also defines requirements for determining the scope of the OH&SMS, as well as general OH&SMS requirements. - Section 5:
Leadership
This clause of the standard requires top management to demonstrate leadership and commitment to the OH&SMS, along with defining the occupational health & safety policy. The top management must also assign process owners with other roles and responsibilities.. - Section 6:
Planning
The planning section defines requirements for addressing risks and opportunities, and the requirements for occupational risk analysis. This clause also includes requirements for hazard identification and assessment, determining legal and other requirements, OH&S objectives and plans for achieving them. - Section 7:
Support
This clause defines requirements for supporting processes and provisions of resources necessary for effective operation of the OH&SMS. It defines requirements for people, infrastructure, work environment, monitoring and measuring resources, competence, awareness, communication and documented information. - Section 8:
Operation
This clause is focused on establishing operational controls to eliminate the occupational health and safety hazards, management of changes and emergency preparedness and response. - Section 9:
Performance evaluation
The purpose of the requirements placed in this clause is to provide the organization with mechanisms to determine the effectiveness of the QMS. It contains requirements for necessary monitoring and measuring, including performance evaluation, compliance obligation, internal audit and management review. - Section 10:
Improvement
The last section of the standard defines requirements for continual improvement of the OH&SMS, including requirements for managing nonconformities, incidents and corrective actions. These sections are based on a Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle, which uses these elements to implement change within the processes of the organization in order to drive and maintain improvements within the processes.
Why is ISO 45001 a good idea for your organization?
There is no doubt that implementation of ISO 45001 brings benefits to the organization. As mentioned before, the number of organizations, both large and small, that have already implemented OHSAS 18001 (which is predecessor of ISO 45001) is already large and still growing. ISO 45001 brings all the benefits of OHSAS 18001, with addition of some new ones.
Here are just a few of these benefits:
- Improve your image and credibility: By assuring customers that you have a commitment to establish and maintain an occupational health and safety management system, you can enhance your image and market share by reducing the number of OH&S incidents on the workplace and sending a clear message that your organization takes care of its employees
- Use evidence-based decision making. By ensuring that you are using accurate data to make your decisions on what to improve, you can greatly increase the chances that your improvements will be successful the first time, rather than having several unsuccessful attempts. By using this data to track your progress, you can correct these improvement initiatives before they go “off the rails,” which can save costs and time.
- Create a culture of continual improvement. With continual improvement, you can work toward better processes and reduced occupational health and safety hazards in a systematic way, in order to improve your public image and potentially reduce your costs. When a culture of improvement is created, people are always looking for ways to make their processes better, which makes maintaining the OH&SMS easier.
- Engage your people. Given a choice between working for a company that shows care and concern for occupational health and safety and one that does not, most people would prefer the first one. By engaging your employees to reduce your occupational health and safety hazards, you can increase theirs focus and retention.
-
In addition to the above-mentioned benefits, the transition from OHSAS 18001 to ISO 45001 brings:
- More clarity on OH&SMS issues
- Enhanced leadership involvement and worker participation in the OH&SMS
- Risk-based thinking for the OH&SMS, as well as for OH&S risks
- Alignment of the OH&S policy and objectives with the strategic direction of the organization
- Integration of the OH&SMS into the business processes of the organization
- Simplified language, common structure and terms.

What are the practical steps to become ISO 45001 certified?
What does it mean to be ISO 45001 certified? The answer to this question depends on the type of the certificate you want to attain. Organizations can get their Occupational Health and Safety Management System certified by certification bodies while individuals can get certified, for example, as ISO 45001 internal and lead auditors. This section provides information on the steps towards the ISO 45001 certification for organizations.
Implementing ISO 45001 standard is a challenging task and the first step is to get the management support for such endeavor. With the top management on board, you can start identifying legal requirements regarding occupational health and safety, define the scope of the OH&SMS and OH&S policy and objectives, identify risks and opportunities and OH&S hazards and define operational controls. There are several mandatory processes that need to be included, and others to be added if the organization finds them necessary.
As part of ensuring consistency of your OH&SMS, you will need to document many procedures and policies that will communicate to the employees what you expect from them in regard to the OH&SMS. The documents can be created internally, or you can seek for external help in form of consultant or documentation templates.
After the organization establishes the processes and necessary documented information, the system will need to operate for some time to determine whether the system is set up properly and whether some changes are necessary. By operating the OH&SMS, the organization will produce records that will demonstrate that the activities are carried out as planned. These records are necessary for auditing and reviewing your system and to achieve certification.
Mandatory steps to finish implementation and get your company certified:
Documenting and implementing the OH&SMS is not enough for the certification. You also need to be sure that it is both effective and compliant with the standard. The following steps are meant to ensure this and prepare your organization for the certification audit:
- Internal audit – The purpose of the internal audit is to determine the level of compliance of your OH&SMS with requirements of the standard. During the audit, the internal auditors will review the documents, records and processes to identify weaknesses and provide information on nonconformity.
- Management review – This is the ultimate review of the effectiveness of your OH&SMS, the top management needs to review the information on OH&SMS performance, results of the internal audits, achievement of the objectives and changes in context of the organization. All this information will enable the top management to make decisions on how to improve the existing OH&SMS.
- Corrective actions – Both the internal audit and management review are providing you with the information on what needs to be changed, corrected and improved. These corrective actions are the best tool for dealing with nonconformity. Corrective actions are taken to achieve full compliance with the standard.
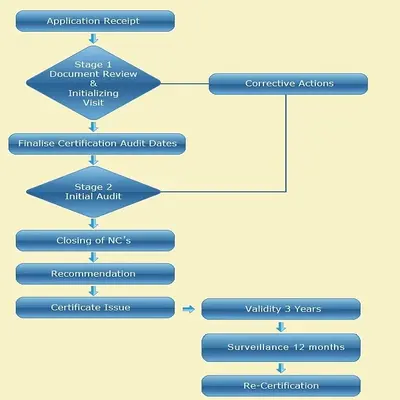
The company certification process is divided into two stages:
- Stage One (documentation review): This is the initial phase of the audit; the certification auditors will review your OH&SMS documents to get familiar with your organization and its processes prior to the main audit and to ensure your documents are compliant with requirements of ISO 45001.
- Stage Two (main audit): The main audit is the most important part of the certification audit. During this phase, the certification auditors will make interviews with the top management and employees and observe your processes. Their goal is to determine the compliance of your OH&SMS not only to requirements of the standard, but also to the content to your documents examined during the first stage.
What ISO 45001 training and certification is available if you’re an individual?
- ISO 45001 Lead Auditor Course. This is the most demanding course. It takes four or five days and provides you with knowledge and understanding of the requirements of ISO 45001 as well as the auditing techniques, sampling records and getting evidence during the audit. If the course is accredited, it enables you to perform certification audits on behalf of the certification body.
- ISO 45001 Internal Auditor Course. This course usually takes two or three days. Unlike the Lead Auditor course, it doesn’t include a competency test and is the most appropriate for persons who want to perform internal audits within their own organizations.
- ISO 45001 Awareness and Implementation Course. There are several courses that provide knowledge of ISO 45001 and how to implement it. These kinds of courses can vary in the length and amount of information provided. They can last from one to five days and include various learning materials, such as e-learning sessions, as a method of teaching the material. Courses like this are the most beneficial for persons who want to get an overview of ISO 450001, or those who will be involved in the implementation or maintenance of the OH&SMS within an organization. Such a course can be more cost-effective than investing in the lead auditor course for those who are involved at this level. There are a number of accredited training organizations around the world where you can gain individual qualifications in ISO 45001.
12 steps for implementation and certification against ISO 4500:
Implementing and gaining certification for an Occupational Health & Safety (OH&S) management system can be tricky, and you might become quickly overwhelmed by the many requirements of the ISO 45001 standard. To help make this easier to understand, the following 12 steps detail some important questions to ask about essential elements of your system.
- Get the support of management: How will you get critical management support ‑ talk to individuals separately, or in a joint meeting?
- Know your legal requirements: Do you have health & safety laws for your industry? Have you looked at the regional, state, national, and international level? Section 6.1.3 of ISO 45001 outlines the requirements for knowing and maintaining your compliance so that your implementation will succeed.
- Define the scope of your OH&S management system: Is your OH&S management system applicable to your entire company, or just one location of a multi-location company? This will be critical for writing your OH&S Policy, and objectives and plans that guide your OH&S management system.
- Define the processes and procedures: What processes and procedures need to be defined to control the OH&S hazards within your company? How will you identify all of your hazards, and the risks associated with them, so that you can ensure the proper controls will be in place? What risk assessment do you need to do? What operational controls and emergency preparedness procedures do you need? What will you write down, and what can be controlled through proper training and awareness?
- Implement the OH&S processes and procedures: What do you need to do to put into place all of the processes and procedures from Step 4? What sort of hierarchy of controls and procedures do you need? Do you need to work closely with some individuals in your organization to achieve success? How will you roll out the additional responsibilities that some employees will now have?
- Train your employees and make them aware: How will you make your employees aware of what ISO 45001 is, and why you are implementing it? Will you have training sessions in department meetings, or will managers train the employees? Who needs to be trained on any changes you have made to the processes? It is important that everyone know how they fit into the OH&S Management system structure.
- Choose your certification body: It is important to choose a certification body suitable for your company to get the most benefit, so how will you do this? Do the auditors know about your industry and the hazards and risks associated with it? What other organizations has the company certified, and what was their level of satisfaction? How does the certification body think that they will provide a benefit to you? These are all questions that you should ask potential certification bodies when you are choosing the right one for you.
- Use the OH&S management system and keep records: As you proceed, what do the OH&S records tell you about your processes? Are they working well, or do you need to modify anything through your corrective action process? Do your employees understand what they need to do, as written in the records, or is there further training needed in some areas? Do you see areas for improvement in your processes, and if so, how can you profit from this? Find out from your certification body how long they need this period to be before they consider the management system mature enough to audit.
- Do your internal audits: Your internal audits are the tools you use to check each of your processes, so what are they telling you? Are your records adequate to show the process is working? Are there any problems that you need to fix with your corrective action process? Do some areas need more frequent audits?
- Do a management review: Is your OH&S management system functioning as expected by the senior management plan? Is it properly implemented and effective? Are improvements being made, and are adequate resources being supplied to the effort? You will only know this by having management review, the output of your management system.
- Corrective actions: Are there problems in your OH&S management system you will need to fix? Did you find these in your process measurements, internal audits, or management review? Have you included OH&S incident investigation in your corrective action system? Use your corrective action process to find the root cause of the problem and address this cause with a corrective action.
- Certification audits: When you are ready, your certification body will send in people to compare your OH&S management system plans, processes, and procedures against the necessary requirements of ISO 45001. Were there any gaps found, and did the auditor’s report highlight these? If so, you will need to correct them and gather the evidence showing that they were addressed. Then, when your system is mature enough, your certification body will conduct the main audit to compare your records to your plans and the ISO 45001 requirements. Did you address any non conformance's in your process data, internal audits, or management reviews? After several days the audit team will issue a report with their findings, including any corrective actions needed. When they are satisfied that your management system addresses the needs of the ISO 458001 requirements, they will issue a recommendation for certification.
Mandatory Documents Required for OHSMS (Occupational Health & Safety Management System) Certification
- OH & S Manual
- OH&S Policy
- Organization Chart
- Identifying interested parties such as neighbors, regulatory bodies, ngo's and employees
- Risk Matrix
- OH&S Objectives and Plans
- ERP Plan & Mock Drill Reports
- HIRA
- Legal Register
- Skill Matrix, Training Records
- Communication Evidence
- ERP Plan & Mock drill reports
- Check lists of equipment's, third party certificates, calibration certificates, etc
- PM Schedule, Calibration Certificates
- Legal Register
- Audit Schedule
- Audit Report
- Minutes of Management Review
- Incidents Register
- Investigation Reports of Incidents
- Action Plans
- Procedure for Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties
- Procedure for Identification and Evaluation of Environmental Aspects and Risks
- Competence, Training, and Awareness Procedure
- Procedure for Communication
- Procedure for Document and Record Control
- Procedure for Internal Audit
- Procedure for Management Review
- Procedure for Management of Nonconformities and Corrective Actions
How to structure documents and records:
ISO 45001 doesn’t have a lot of requirements regarding documentation, so it is imperative that you optimize the volume of your OH&SMS documentation by trying to develop documentation that meets all requirements, while remaining simple and light. Instead of just documenting every single requirement of the standard, the organization should focus on the most important information and provide a sufficient amount of information to its employees to ensure compliance with the standard and legal requirements.
The following recommendations take into consideration the best practice in developing OH&SMS documentation:
- 1.OH&S Manual:The manual is not a mandatory document, but very often is an essential part of the OH&SMS. This document is a summary of your entire OH&S management system with reference to the procedures and records within the system, and it is a good place to put all important information that didn’t fit into any other document of your OH&SMS. For more information, see Does your organization need a health & safety manual?
- 2.Procedure for Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties: Occupational Health and Safety Management System, and it can be a good idea to document not only the results of determining the context, but also the process itself. This document can define what elements of the context need to be considered, who will participate, what methodologies will be used, and how often information on the context will be revised. The Procedure for Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties can be of great help in initial implementation of the standard and these new requirements. For more information, see: Defining the context of the organization according to ISO/DIS 45001 and Determining interested parties according to ISO 45001.
- 3.OH&S Scope: This document is usually rather short and is written at the beginning of the ISO 45001 implementation. Normally, it is a stand-alone document called Scope of the OH&SMS, although it can be merged into an OH&S Manual, which defines the limitations of the OH&S management system within your company, and identifies what elements are included and how they interact. Learn more about the OH&S Scope in the article: How to determine scope of the OH&SMS..
- 4.OH&S Policy: The OH&S Policy is intended to be a company’s documented intention to meet legal compliance, prevent occupational health and safety hazards, and continually improve. The Policy is a focus for the company to work toward and should readily convey the goal of the organization. It is often documented in an OH&S Manual and sometimes posted throughout the organization as a way of communicating to all employees, because it is important that every employee understand how the Policy relates to his or her job. For more information, see How to write an OH&S Policy.
- 5. Roles and responsibilities within the OH&SMS: There are two options for documenting this requirement. The first is to have a general document that will define roles and responsibilities within the OH&SMS for the entire organization. The second is to have roles and responsibilities documented within different OH&S documents, such as procedures and work instructions. Both approaches are OK, and it is up to the organization to decide what is the most appropriate approach.
- 6.Consultation and participation of workers: The standard requires the organization to implement, establish, and maintain a process for consultation and participation of workers at all applicable levels and functions in development, planning, implementation, performance implementation, and actions for improvement of the OH&SMS. Although it is not required, it can be beneficial to the organization to document the mechanisms and resource provision for the consultation and participation and define the responsibilities. If you want to decrease the documentation, this procedure can be merged with the communication process into the Procedure for Communication, Participation and Consultation.
- 7.Methodology and criteria for assessment of OH&S risks: In order to address risks and opportunities, the organization needs to identify them first and assess what risks and opportunities are worth addressing.
- 8.Process for addressing OH&S risks and opportunities: Unlike other management system standards that follow Annex SL and the High-Level Structure defined by the ISO, ISO 45001 requires the organization to document the process for addressing risks and opportunities.
- 9.Procedure for Hazard Identification and Assessment: The methodology and criteria for assessment of occupational health and safety hazards is often a legal requirement, so the standard doesn’t require this procedure explicitly.
- 10.Legal and other requirements: It is important for your company to know and understand the legal requirements that apply to your business practices.
- 11.OH&S objectives and plans for achieving them: The objectives are derived from the goal stated in the OH&S Policy, and are the main method used by companies to focus this goal into plans for improvement.
- 12.Evidence of competence: Keep records to prove that you identified what competencies are required for the crucial processes in your OH&SMS, and how employees met these competencies.
- 13.Communication process: ISO 45001 requires the organization to perform communication, participation, and consultation with employees, subcontractors, and relevant external parties on issues regarding occupational health and safety.
- 14.Procedure for Document and Record Control: How do you approve, update, and re-approve your documents?
- 15.List of External Documents: Although this record is not explicitly required, the standard requires external documents necessary for the OH&SMS to be identified and controlled.
- 16.Procedure for Operational Planning and Control: When you have identified that your operations can have a negative impact on occupational health and safety, you need to put controls in place to mitigate the risks and prevent the injuries and health problems from happening.
- 17.Procedure for Change Management: The standard requires the organization to implement a process for controlling and planning temporary and permanent changes in the OH&SMS.
- 18.Emergency preparedness and response process: When there is a risk that an emergency might happen (such as a chemical spill), you need to have plans in place to respond and react to the emergency and limit the environmental damage you will cause.
- 19.Monitoring, measuring and analysis of OH&S performance: When you identify a key characteristic of a process, you will also need to determine whether this characteristic can have a significant OH&S risk if it is not controlled by the company.
- 20.Maintenance, calibration or verification of monitoring equipment: In your processes, you may need to monitor and measure critical elements of the OH&SMS to ensure compliance with legal requirements.
- 21.Internal audit: How do you audit your Occupational Health & Safety Management System to make sure that it is performing as planned and is effective?
- 22.Management review: It is recommended for organizations to have a procedure for management review where the organization can define the inputs and outputs of the management review.
- 23.Incident investigation and reporting: Occupational health and safety incidents are big problems for the organization, even if they don’t result in injuries of the employees.
- 24.Management of Nonconformities and Corrective Actions: With the Occupational Health & Safety Management System, you will find that you have non-conformances occur within your you will need to correct, and when you investigate the root causes of these problems you will have corrective actions taken.
- 25.Evidence of the results of continual improvement: This is a completely new requirement aiming to ensure that the organization takes actions towards improvement of its OH&SMS and to provide evidence that those actions are taken.