What is ISO?
ISO is the International Organization for Standardization, it is Non-Governmental Organization that structures an extension between the public and private divisions, Its work from Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland and was established in 1947 to create basic worldwide benchmarks in numerous regions. ISO is a system of the national guidelines establishments of with 163 part's nations.
Introduction :
It is widely accepted that environmental issues are increasingly influencing the future strategic direction of every business around the globe. Being aware of environmental impacts that humanity is experiencing, such as climate change and biodiversity loss, in addition to the growth in demand of natural resources as vital as water, drive some organizations to incorporate this “environmental thinking” into their activities. These so-called “green companies” go this direction not just to contribute to environmental protection, or to help their companies to survive in the market, but to grow in this relatively new and adverse situation. Having said this, what role can ISO 14001:2015 play in a company’s environmental thinking? An Environmental Management System (EMS) can be used for managing the impact of a company’s activities on the environment and, in consequence, contribute to the continual improvement of its environmental performance. This white paper will help you to understand how your business can grow through implementing an EMS.
Who is ISO 14001 Applicable to?
Many companies wonder if ISO 14001 can be applied to their specific activities or type of industry. In fact, an Environmental Management System can be used in any kind of organization to enhance its environmental performance regardless of its size, sector, legal form, geographical location, or the product or service that it provides. The flexibility that the standard allows an organization in relation to the implementation of its Environmental Management System requirements makes ISO 14001 the best option for demonstrating the company´s contribution to the protection of the environment. For instance, because the organization decides where to implement the standard, it can implement it in the whole business or just in a part of it – for example, just one location if it is a multi-site company, or just one product or one department (e.g., production). However, your company will need to comply with all the applicable ISO 14001 requirements to claim conformity to the standard.
What is an Environmental Management System?
An Environmental Management System is a framework used by organizations to achieve their environmental aims throughout consistent assessment, monitoring, and improvement of their environmental performance. It consists of a set of policies, processes, procedures, and records that determine the internal rules that a company follows to protect the environment. Each organization tailors the Environmental Management System to its own needs and objectives. This means that every company decides about the level of environmental performance that it wants to achieve. In this sense, ISO 14001 gives you the guidelines to follow for a correct implementation and creation of an Environmental Management System. The most widely used standard for the development of an Environmental Management System is ISO 14001, and it is part of the family of ISO 14000 standards dedicated to environmental management. According to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), more than 300,000 companies have been certified against ISO 14001 in 171 countries.
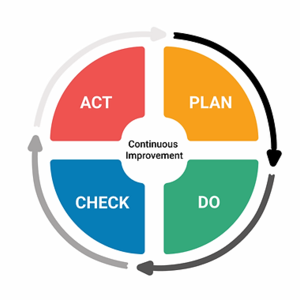
The importance of the PDCA cycle:
ISO 14001 is a proactive tool based on a continual improvement approach in regard to environmental issues. This is accomplished through a Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle that consists of four steps, including:
- Plan:
Establishing the plans for improvement of environmental performance - Do:
Implementing the processes that have been defined in the plans - Check:
Reviewing the processes regularly to make sure they are being followed as originally planned - Act:
Taking the necessary actions to achieve the continual improvement of the system.
This PDCA cycle should be implemented in every aspect and process of your organization so that it can help your organization to increase efficiency and contribute to the growth of your business.
WHAT BENEFITS DOES ISO 14001 BRING TO YOUR BUSINESS?
It might be surprising, but many benefits can arise from implementing the standard in your company – and not only the obvious one of contributing to protecting the environment. These benefits are the main reasons to implement the standard and, therefore, to improve the environmental performance of a company. Below you will find some of the most remarkable benefits that can apply to your organization:
- Improve your reputation:
Today’s organizations need to address environmental expectations from stakeholders, including customers, non-profit organizations, neighbors, and others, if they don´t want to be at risk of losing their position in the marketplace. A good way to demonstrate commitment to environmental protection is by implementing an Environmental Management System, which will improve your corporate image and reputation among all these interested parties. In addition, because ISO 14001 is an internationally recognized standard, many contracts or tenders require companies to be certified in ISO 14001, so it can also be seen as a marketing tool to enhance your image and credibility and gain new contracts. - Comply with applicable statutory and legal requirements:
Implementing an Environmental Management System in your organization will definitely help you to comply with statutory and legal requirements. It will also assist you with monitoring your compliance in a systematic way and to identify new legislation with enough time to make the necessary adjustments in the business. As a consequence, on the one hand you will improve your corporation’s image, while on the other hand, you will avoid costly fines coming from a legal breach that may occur. - Reduce your costs and improve efficiency:
One of the main benefits of incorporating an Environmental Management System in your business strategy is avoiding risks related to any environmental incident, thereby reducing costs related to fines or reparations. Also, improving the efficiency and performance of your business activities, in terms of reducing the use of natural resources (i.e., water), energy, and waste, will significantly lessen related expenses. - Assure a continual improvement culture:
Being one of the most remarkable ISO 14001 principles, adopting a continual improvement culture will help the company to gain more efficiency in its processes, increasingly cutting costs and reducing the recovery time when problems arise. This continual improvement can be achieved thanks to gathering accurate data, which can be used to track any change and compare different situations that may happen in the organization. - Gain new customers:
In response to a growing green supply chain, many suppliers are asked to comply with an environmental standard. In this sense, ISO 14001 certification is definitive proof of managing and mitigating environmental impacts in a business. In addition, when applying for a new contract, sometimes companies are asked to be ISO 14001 certified, so implementing an Environmental Management System means a clear competitive advantage in the actual marketplace. - Engagement of employees:
Getting employees involved in the improvements of the activities that they perform in their work contributes to their engagement in the business, positively influencing employee morale and reducing turnover. When people feel happier in their work, they are more productive in their position. As a consequence, there is an important impact in the company, reducing expenses related to hiring new personnel who need to be trained.
ENSURING PROFIT-MAKING WITH ISO 14001:
Profit-making is a consequence of the successful integration of the Environmental Management System into the strategic direction of the organization. The following aspects related to different clauses of the standard are the key to increasing profits in the company:
- Identification and evaluation of the company´s risks and opportunities:
Determining which are the significant risks and opportunities in your company will greatly drive the organization to improve the system and, therefore, to increase their profit-making. Fixing or repairing is always more expensive than preventing possible risks, so you will avoid unnecessary costs derived from unexpected incidents arising from environmental aspects. - Planning the necessary resources:
Consider the resources needed for the implementation, certification, and maintenance of the Environmental Management System in terms of financial resources (consultant fees, audit costs, etc.) and time dedicated by personnel. Also, estimate the time frame to finish your implementation, which will help you to define a project plan for establishing milestones and responsibilities. You can be guided by similar companies that have already implemented the standard. - Providing training and ensuring environmental awareness:
Training your employees to perform the processes in compliance with the ISO 14001 requirements is crucial for the successful operation of the Environmental Management System. At the same time, environmental awareness is necessary from the top management all the way to the shop floor to ensure their engagement and cooperation with the implementation and maintenance of the standard. - Applying continual improvement:
This principle remains one of the most relevant when it comes to profit-making. Following the Plan-Do Check-Act cycle will help to improve the activities carried out in your company and, therefore, the organization will be able to see the positive results regarding cost and return on the Environmental Management System investment. - Conducting performance evaluation:
Performance evaluation will ensure profits for the organization. Using key performance indicators (KPIs) that can be measured to assess how your company is doing will help your company to check if the organization is making real signs of progress and achieving what it has already planned. This profit-making has been demonstrated through some formal studies. According to the already mentioned research paper about sustainability of positive relationship between environmental performance and profitability of SMEs, there is a positive relationship in small and medium-size companies between their environmental performance and their profitability.

Mandatory Documents Required for EMS (Environment Management System) Certification
- EHS Manual
- Environmental Policy
- Identifying interested parties such as regulatory bodies, neighbors, employees, ngo's
- Risk Matrix
- Aspect-Impact Register
- Significant Environmental Aspects
- Environmental Objectives and Plans
- OCP
- ERT Team, ERP Plan & Mock Drill Reports
- Legal Register
- Skill Matrix, Training Records
- Communication evidence such as notice boards, emails, any bulletin
- Checklists, Compliance Registers, Third-Party Certifications, Calibration
- Audit Programme
- Audit Report
- Minutes of Management Review
- Action Plans
- Procedure for Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties
- Procedure for Identification and Evaluation of Environmental Aspects and Risks
- Competence, Training, and Awareness Procedure
- Procedure for Communication
- Procedure for Document and Record Control
- Procedure for Internal Audit
- Procedure for Management Review
- Procedure for Management of Nonconformities and Corrective Actions
How to structure documents and records ?
Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties: This is a new requirement of the standard and it is a good idea to document the process of determining the context and identifying interested parties and their expectation since it is done for the first time. This document should include all internal and external issues to be considered as well as the process and responsibilities for identification of interested parties and their needs and expectations. Procedure for Determining Context of the Organization and Interested Parties can be of great help in implementation of these new requirements.
- EMS Scope:
This document is usually rather short, and written at the beginning of the ISO 14001 implementation. Normally, it is a stand-alone document called Scope of the EMS, although it can be merged into an Environmental Manual, this defines the limitations of the environmental management system within your company, and identifies what elements are included and how they interact. - Environmental Policy:
The Environmental Policy is intended to be a company’s documented intention to meet legal compliance, prevent pollution, and continually improve. The Policy is a focus for the company to work toward and should readily convey the goal of the organization. It is often documented in an Environmental Manual and sometimes posted throughout the organization as a way of communicating to all employees, since it is important that every employee understand how the Policy relates to his or her job. - Risks and Opportunities that need to be addressed:
According to the 2015 revision of ISO 14001, the risks and opportunities regarding the EMS must be identified and addressed, but there is no requirement to use any methodology or write a procedure. The standard only requires risks and opportunities that need to be addressed to be documented. The process of addressing risks and opportunities includes consideration of internal and external issues relevant to the EMS, interested parties, scope of the EMS as well as the environmental aspects and compliance obligation. The easiest way to fulfill this requirement is to merge the risk and opportunities addressing process with identification and evaluation of environmental aspects. - Procedure for Identification and Evaluation of Environmental Aspects (with criteria for determining significance):
ISO 14001:2015 require companies to document all environmental aspects in the company and associate them with environmental impacts, and also significant environmental aspects and criteria for determining significance of the aspects. The best way to document the criteria is through Procedure for Identification and Evaluation of Environmental Aspects and Risks, documenting environmental aspects and impacts, together with significant environmental aspects can be done through Process Aspects Chart. - Compliance Obligation record:
It is important for your company to know and understand the legal requirements that apply to your business practices. To make this work you need to devise a way to ensure you know which laws apply, and how you will keep up to date on legal changes. Beside legal obligations the obligations towards other interested parties must be identified as well. This is a part of identification of interested parties and their needs and expectations so it should be done during this process. The standard requires compliance obligations to be documented and evaluated on regular basis. -
Environmental Objectives and Plans for Achieving Them:
The objectives are derived from the goal stated in the Environmental Policy, and are the main method used by companies to focus this goal into plans for improvement. The objectives are intended to be S.M.A.R.T. (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-based) and should have relevance at all levels of the company, meaning that all employees should understand how their jobs support meeting the environmental objectives and targets. - Competence, Training and Awareness records:
Introducing environmental practices in an organization often requires additional training of relevant employees. The best way to define this process is by procedure that defines identification of training needs, training planning, conducting and evaluation of training effectiveness as well as assigning responsibilities for this. Although it is not requirement of the standard, the good practice shows that Procedure for Competence, Training and Awareness can be of great help to organization. The standard explicitly requires only the evidence of competence and that is Training Record. - Evidence of EMS Communication:
Hand in hand with awareness is how you will communicate to internal and external parties. How will you do this, and what information needs to be communicated? The standard only requires organization to keep evidence of its communication, as appropriate but considering the importance of communication process in EMS, it is recommended to have documented Procedure for Communication that describes it. - Procedure for Control of Documents and Records:
How do you approve, update, and re-approve your documents? When a document is changed, how do you identify changes, and make sure that people who need the current document have it and stop using older documents? How do you make sure the documents can be read, and how do you control documents that come from outside of your organization for use? How do you maintain your records that show your EMS is implemented and maintained, including how you identify, store and protect the records so that they can be retrieved as necessary, for the correct amount of time, and destroyed when no longer needed but not before? - Operational control procedures:
When you have identified that your operations can have a negative impact on the environment (also called a significant environmental aspect), you need to put controls in place to ensure the impact does not happen and the environmental damage does not occur. In order to have a known and consistent way of doing what is needed to avoid the occurrence, you will need to create operational control procedures. If no situations are present, you need to ensure that there is no deviation from the policy, objectives & targets, or related significant aspects, and these procedures are not required. - Procedure for Emergency Preparedness and Response:
When there is a risk that an emergency might happen (such as a chemical spill), you need to have plans in place to respond and react to the emergency and limit the environmental damage you will cause. Also it is necessary to ensure that the emergency plan will be followed by the employees, and this is done by testing the emergency response plans and periodically review and revise the process and plans Learn more with ISO 14001 emergency preparedness and response and 5 steps to set up an emergency plan according to ISO 14001. - Monitoring performance information:
When you identify a key characteristic of a process, you will also need to determine whether this characteristic can have a significant environmental impact if it is not controlled by the company. When this is the case, the organization needs to document what information needs to be monitored so that employees can react to changes in performance and avoid the environmental impact. - Calibration records:
In your processes, you may need to monitor and measure critical elements of the EMS to ensure compliance with legal requirements. As an example, you may need to measure the concentration of a chemical in your wastewater. When you do this, you need to use calibrated equipment to ensure your measurements are accurate, and maintain records of these calibrations. - Internal audit:
How do you audit your environmental management system to make sure that it is performing as planned and is effective? Who is responsible for planning and carrying out the audits? How do you report results and what records are kept? How do you follow up on corrective actions noted in audits? Learn more in this article about the Internal Audits in the EMS: Five main steps. Keep records of these activities to show EMS conformance and improvement. - Nonconformity and corrective action:
What controls are in place, and who is responsible, to make sure that environmental non-conformity is addressed? How do you ensure that corrections are made, and what records are kept of the process? - Corrective Actions:
How do you review non-conformities, determine causes, and evaluate the need for actions to correct them? How do you implement the necessary actions, review that the actions were effective, and keep records of the actions taken? With the environmental management system you will find that you have non-conformances occur within your processes that you will need to correct; and when you investigate the root cause of these problems you will have corrective actions and preventive actions taken. You will need to keep records of these activities to show improvement. Learn how to do this with Corrective and Preventive Actions to support Environmental Management.
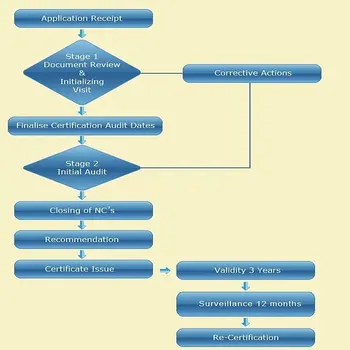
List of ISO 14001 implementation steps:
- Obtain management support –
Management support is critical. Without this support your implementation of ISO 14001 will almost certainly fail. You need to have a good sales pitch to convince your management that ISO 14001 is a good idea. - Identify legal requirements –
Making sure that you have identified the legal and other requirements for your EMS is another crucial step to make sure your implementation succeeds. - Define EMS scope –
To ensure you know the limits of what needs to be done, you need to define the scope of your EMS. This helps prevent the inclusion of areas of your business that might not have an effect on the environment. The key tools to define the scope are the environmental policy and environmental aspects (the interaction you have with the environment); these are the first documents you will need to create for the EMS. - Define EMS procedures and processes –
These will include the processes and procedures you will identify as necessary to ensure consistent and adequate results when preventing negative environmental impacts and to respond to emergency situations. - Implement EMS procedures and processes –
Often, these processes will be linked to the processes that are already in place at your organization, such as the tracking of waste from your facility. Since not all processes need to be documented procedures, it is important to decide which ones must be documented in order to prevent environmental damage. - Perform training and awareness –
Employees should have training on what ISO 14001 is and why you are doing this, in addition to training for any changes to the processes they are involved in. It is important that everyone in your organization knows what you are doing with your EMS and how they fit into the equation. - Choose a certification body –
The certification body is the company that will ultimately come in to audit your EMS processes for compliance with ISO 14001 requirements, as well as whether the system is effective and improving. It is best to interview several certification bodies to decide which is right for your company, since this can be a very important step in how effective your implementation is. - Operate the EMS : measure and keep records – –
This is when you will collect the records that will be required during an audit to show that your processes meet the requirements set out for them. The records also show that the processes are effective and that improvements are being made in your EMS as needed. Certification bodies will identify a certain length of time for this to happen in order to ensure that the system is mature enough to show compliance. - Perform internal audits –
The certification body will want you to audit each process internally before they come in to do the certification audit. This will give you a chance to make sure that the processes are doing what you had planned, and if not, you will have a chance to fix any problems that you find. - Perform management review –
Just as important as the support that management gives for the implementation of ISO 14001, is the involvement of management in the continued maintenance of the EMS. In order to ensure that the processes have adequate resources to be effective and improve, management needs to review specified data from the activities of the EMS and react to that data appropriately. - Implement corrective actions –
In order to fix problems and improve the system, you need to use corrective actions to find the root cause of any problems found and take action to correct that root cause. These problems can be identified during your measurements, internal audits, and management review. - Certification audit – Stage 1 –
Here the certification body will review your documentation to verify that, on paper, that you have addressed all the necessary requirements of the ISO 14001 standard. The auditors will issue a report outlining where you comply and where there are problems, so that you have a chance to implement any corrective actions to address the problems. - Certification audit – Stage 2 –
During this main audit the certification body auditors will perform the on-site audit where they will review the records you have accumulated by operating your EMS processes, including your records of internal audits, management review, and corrective actions. After this audit, done over several days, they will issue a report detailing their findings and whether they have found your EMS to be effective and in compliance with the ISO 14001 requirements. The auditors will also make a recommendation for certification if you meet all requirements; however, if you have any major non-conformances then you will need to resolve the corrective action for these problems before certification can be recommended.
CONCLUSION:
The main concern in relation to ISO 14001 certification in organizations is the cost of the implementation. Many expenses need to be considered during the implementation, such as training for the employees, updating the equipment, etc. However, implementing the standard can have many advantages that greatly outweigh the challenges faced by the organizations. Some studies have demonstrated that the companies that have successfully integrated ISO 14001 into their operations see a positive impact in their financial situation, showing that an EMS can help organizations to grow and increase their competitiveness in the marketplace. ISO 14001 should be considered a proactive and powerful tool that responds to an increasing demand for green company behavior, turning challenges into opportunities, such as cost savings, operational efficiency, legal compliance, and waste reduction.