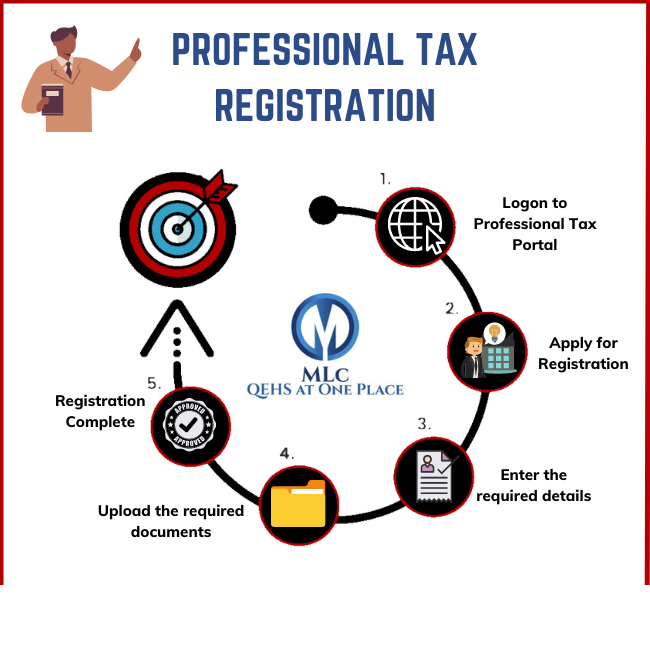
About Professional Tax
If you ever take a look at your payslips, you will notice a small deduction mentioned along with all the HRA, conveyance, and basic salary breakups. This deduction is generally to the tune of INR 200 or so and is called the professional tax. This tax varies by state, and in some places, there may be no deduction. So, what is professional tax?
What is Professional Tax?
The respective state governments in India levy the professional tax on income from profession or employment. The professionals earning an income from salary or other practices such as a lawyer, teacher, doctor, chartered accountant, etc., are required to pay professional tax. It is deducted by the employer and deposited with the state government. Other individuals pay it themselves. The tax has a maximum limit of INR 2500/- per year.
Professional Tax Registration and Returns
Professional Tax Registration is mandatory within 30 days of employing staff in a business or, in the case of professionals, 30 days from the start of the practice. Professional tax needs to be deducted from the salary or wages paid amount. Application for the Registration Certificate should be made to the assesses state tax department within 30 days of employing staff for his business. If the assesses has more than one place of work, then application should be made separately to each authority with respect to the place of work under the jurisdiction of that authority.
If an employer has employed more than 20 employees, he is required to make the payment within 15 days from the end of the month. However, if an employer has less than 20 employees, he is required to pay quarterly (i.e. by the 15th of next month from the end of the quarter).
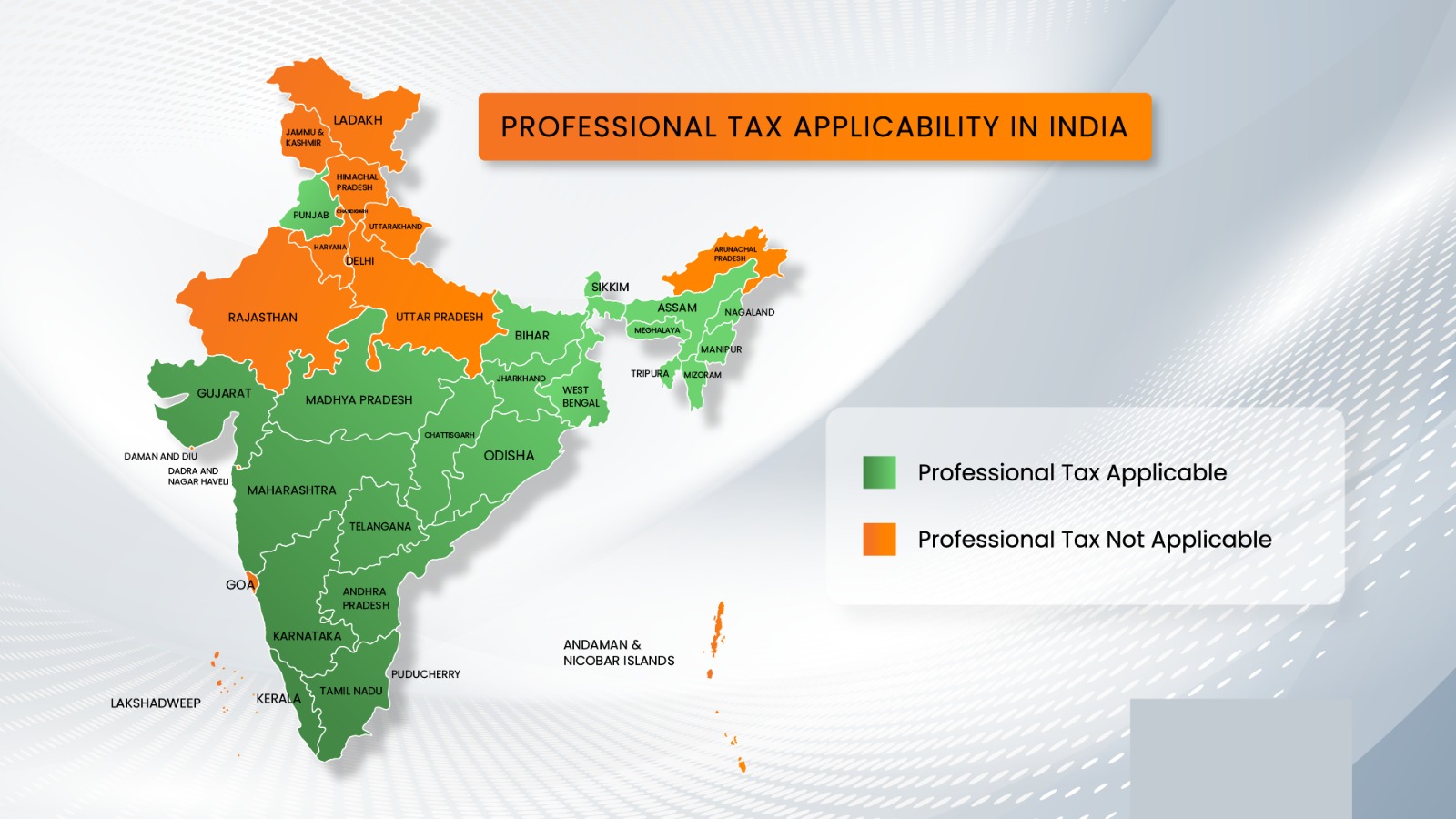
Professional Tax Applicable States Across India
The states which impose professional tax in India are:
| Applicable States | Not Applicable States |
|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | Central |
| Assam | Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Bihar | Arunachal Pradesh |
| Gujarat | Chandigarh |
| Jharkhand | Chhattisgarh |
| Karnataka | Dadra and Nagar Haveli |
| Kerala | Daman and Diu |
| Madhya Pradesh | Delhi |
| Maharashtra | Goa |
| Manipur | Haryana |
| Meghalaya | Himachal Pradesh |
| Mizoram | Jammu and Kashmir |
| Nagaland | Ladakh |
| Odisha | Lakshadweep |
| Puducherry | Rajasthan |
| Punjab | Uttar Pradesh |
| Sikkim | Uttarakhand |
| Tamil Nadu | |
| Telangana | |
| Tripura | |
| West Bengal |
Exemptions
There are exemptions provided for certain individuals to pay Professional Tax under the Professional Tax Rules. The following individuals are exempted from paying Professional Tax:
- Parents of children with permanent disability or mental disability.
- Members of the forces as defined in the Army Act, 1950, the Air Force Act, 1950, and the Navy Act, 1957, including members of auxiliary forces or reservists serving in the state.
- Badli workers in the textile industry.
- An individual suffering from a permanent physical disability (including blindness).
- Women exclusively engaged as agents under the Mahila Pradhan Kshetriya Bachat Yojana or Director of Small Savings.
- Parents or guardians of individuals suffering from mental disability.
- Individuals above 65 years of age.
Who is Responsible?
The employer is responsible for deducting professional tax from the salaries of his employees and paying the amount so collected to the appropriate state government. An employer has to furnish a return to the tax department in the prescribed form within the specified time along with proof of tax payment.
Professional Tax in India
The maximum amount of Professional Tax that can be imposed by any state in India is INR 2500/-. Total amount of Professional Tax paid during the year is allowed as deduction under the Income Tax Act. The Professional Tax is a source of revenue for the state governments which helps in implementing schemes for the welfare and development of the region. Professional Tax is deducted by the employers from the salary of the salaried employees, and is deposited with the state government. Other individuals, pay it directly to the government or through the local bodies appointed to do so.
Consequences
- Fails to Get Registration
- He will be liable to a penalty for the period during which he remains unregistered.
- Fails to Deposit to the Government/ Late Deposition
- He will be liable to a penalty for the period during which he remains unregistered.
- Non-Deposition of Amount.
- The officials have power to recover such amount along with applicable penalty and interest from the assets of such defaulter. Moreover, they can attach his bank account also. In serious cases, prosecution case also can be filed.